Introduction
Kubernetes is the leading container orchestration platform used by companies worldwide to manage containerized applications. The Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer (KCAD) are crucial for engineers and managers aiming to showcase their expertise in deploying and managing Kubernetes clusters and applications. Whether you’re looking to advance your career in DevOps, cloud computing, or software engineering, these certifications can be a stepping stone to achieving your professional goals.In this guide, we will walk you through everything you need to know about the Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer certifications, including the skills you’ll gain, preparation plans, and more. We’ll also guide you through the certification tracks, help you identify your learning path, and answer some common questions.
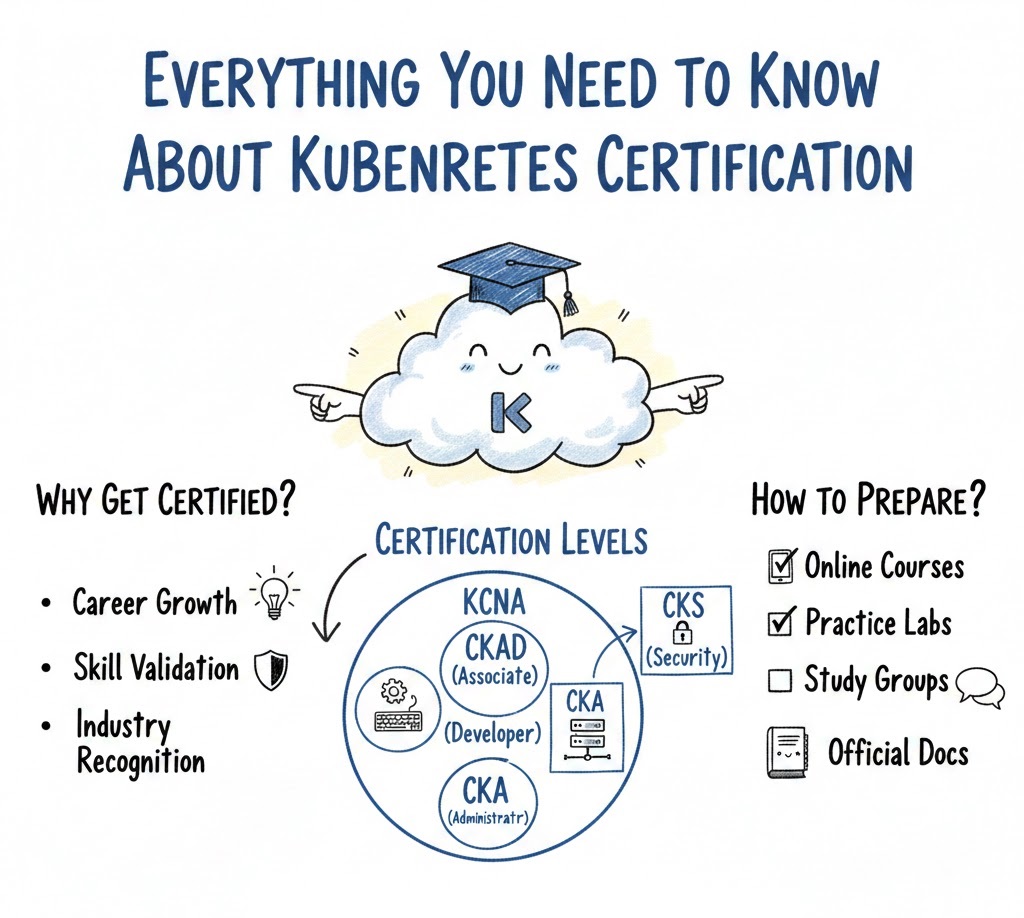
What Is Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer?
The Kubernetes Certified Administrator (K8s-CA) and Kubernetes Certified Developer (K8s-CD) certifications validate your ability to administer and develop Kubernetes-based applications and clusters.
The Administrator exam focuses on Kubernetes architecture, deployment, and configuration of clusters, while the Developer exam targets your ability to design, build, and troubleshoot applications within Kubernetes.
Who Should Take the Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer Certifications?
These certifications are ideal for professionals who are looking to:
- Transition to Kubernetes-based environments.
- Expand their skill set in cloud-native technologies.
- Enhance their career in DevOps, platform engineering, or cloud management.
The certification exams are suited for the following profiles:
- DevOps Engineers
- Cloud Engineers
- Platform Engineers
- Security Engineers
- Software Developers
Skills You’ll Gain
The Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer certifications will equip you with the skills to manage Kubernetes clusters, deploy applications, and automate operations. You’ll become proficient in using tools like kubectl and Helm, configuring clusters, scaling apps, and ensuring security, all essential for modern DevOps and cloud engineering roles.
- Kubernetes Cluster Management
- Application Deployment on Kubernetes
- Resource Management (CPU, Memory, Pods, etc.)
- Troubleshooting and Debugging Kubernetes Issues
- Networking and Security in Kubernetes
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) in Kubernetes
- Working with Kubernetes CLI (kubectl)
- Service Discovery and Load Balancing in Kubernetes
Real-World Projects You Should Be Able to Do After the Certification
- Deploying highly available Kubernetes clusters.
- Building CI/CD pipelines to automate deployment in Kubernetes.
- Managing Kubernetes workloads and ensuring high availability.
- Implementing monitoring and logging for Kubernetes clusters.
- Securing a Kubernetes environment by managing roles and access.
- Automating routine Kubernetes tasks using Helm or other tools.
Preparation Plan
7-14 Days (Fast Track)
- Key Areas: Kubernetes basics, setup of Kubernetes clusters, YAML files.
- Practice: Learn to deploy basic apps, use kubectl commands, and set up a Kubernetes environment.
30 Days (Balanced)
- Key Areas: Advanced configuration, debugging, and security in Kubernetes.
- Practice: Hands-on with persistent storage, networking, and managing multiple environments.
60 Days (Advanced)
- Key Areas: Complex deployments, Helm, scaling Kubernetes applications, managing enterprise-grade clusters.
- Practice: Work on real-world projects like setting up multi-cluster environments and implementing CI/CD pipelines.
Common Mistakes
- Skipping Basics: Rushing into advanced topics without understanding core concepts.
- Lack of Hands-On: Not spending enough time practicing on real Kubernetes environments.
- Not Using the Right Tools: Not getting familiar with kubectl, Helm, or other essential tools.
- Misunderstanding Cluster Architecture: Not fully understanding the different components and their interactions.
- Skipping Security Considerations: Focusing only on functionality and not on securing clusters.
Best Next Certification After This
- Same Track: Master in Kubernetes Engineering.
- Cross Track: DevOps Certified Professional (CDP), Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS).
- Leadership: DevOps Architect Certification.
Choose Your Path: Learning Paths
The Kubernetes certifications open various learning paths based on your career aspirations. Here are six key paths to consider:
FinOps: Focus on cost management in cloud environments using Kubernetes. Learn how to optimize the financial aspect of Kubernetes clusters, ensuring efficient cloud resource usage without overspending.
DevOps: Dive into Kubernetes to automate deployments, manage containerized applications, and integrate with CI/CD pipelines. This path helps you streamline workflows and improve the software delivery process.
DevSecOps: Focus on security within Kubernetes environments. Learn how to secure containerized applications, manage vulnerabilities, and implement compliance policies to ensure robust, secure systems.
SRE (Site Reliability Engineering): This path emphasizes using Kubernetes for maintaining application reliability, scalability, and uptime. It’s perfect for professionals looking to manage large-scale systems efficiently.
AIOps/MLOps: Aimed at automating IT operations with artificial intelligence, this path teaches you how to deploy and manage machine learning models on Kubernetes, ensuring smooth and efficient operations.
DataOps: This path equips you with the skills to manage and optimize data workflows using Kubernetes, helping you scale data pipelines, ensure reliability, and handle real-time processing.
Role → Recommended Certifications
| Role | Recommended Certifications |
|---|---|
| DevOps Engineer | Master in DevOps Engineering, Kubernetes Certified Administrator |
| SRE | Kubernetes Certified Administrator, Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist |
| Platform Engineer | Kubernetes Certified Developer, Master in Kubernetes Engineering |
| Cloud Engineer | Master in Cloud Engineering, Kubernetes Certified Administrator |
| Security Engineer | Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist, DevSecOps Certified Professional |
| Data Engineer | DataOps Certified Professional, Kubernetes Certified Developer |
| FinOps Practitioner | FinOps Certified Practitioner, Kubernetes Cost Management |
| Engineering Manager | Master in DevOps, Kubernetes Certified Administrator |
Kubernetes Certified Administrator vs. Kubernetes Certified Developer
| Feature | Kubernetes Certified Administrator | Kubernetes Certified Developer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Cluster management, administration, and troubleshooting | Application development, deployment, and debugging on Kubernetes |
| Target Audience | System administrators, DevOps engineers, cloud engineers | Software developers, DevOps engineers, platform engineers |
| Primary Skills | Cluster configuration, network management, storage, and security | Application containerization, resource management, and troubleshooting |
| Exam Duration | 3 hours | 3 hours |
| Prerequisites | Basic knowledge of Kubernetes and containerization | Familiarity with Kubernetes concepts and application deployment |
| Key Tools Used | kubectl, Helm, kubeadm, Kubernetes CLI | kubectl, Helm, Docker, Kubernetes API |
| Job Role | Kubernetes administrator, DevOps engineer, platform engineer | Kubernetes developer, software engineer, DevOps engineer |
| Certification Objective | Demonstrate the ability to deploy, manage, and troubleshoot Kubernetes clusters | Show expertise in building, deploying, and maintaining applications on Kubernetes |
FAQs
1. How difficult is the Kubernetes Certified Administrator exam?
The exam is considered moderately difficult and requires in-depth knowledge of Kubernetes architecture, deployment, and management.
2. How much time should I spend preparing for the exam?
The preparation time varies, but most candidates spend 2-3 months preparing.
3. Are there any prerequisites for taking this certification?
No formal prerequisites are required, but familiarity with Linux, containers, and cloud environments will help.
4. How do I register for the exam?
You can register on the official Kubernetes certification website.
5. Is hands-on experience necessary?
Yes, hands-on experience is crucial to understanding Kubernetes concepts and passing the exam.
6. What resources should I use to study for this certification?
Use online courses, official documentation, and hands-on labs.
7. Can I retake the exam if I fail?
Yes, you can retake the exam by paying the exam fee again.
8. What is the value of this certification in the job market?
Kubernetes certifications are highly valued in DevOps and cloud engineering roles, offering career advancement opportunities.
9. What skills will I gain from the Kubernetes Certified Developer exam?
You’ll gain skills in deploying and managing applications on Kubernetes, optimizing resource utilization, managing storage, and troubleshooting application performance.
10. How is the exam environment structured?
The exam is conducted remotely, using a web browser where you access a live Kubernetes environment to perform the required tasks. You are given 3 hours to complete the exam.
11. What happens if I don’t pass the Kubernetes exam?
You can retake the exam after paying the fee again. Make sure to review areas where you faced challenges and practice further before retaking the exam.
12. What are the career benefits of getting Kubernetes certified?
Kubernetes certifications open doors to higher-paying jobs in DevOps, cloud computing, software development, and system administration. They showcase your expertise in modern container orchestration and cloud-native technologies.
FAQs on Master in Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer
- What is the main difference between the Administrator and Developer exams?
The Administrator exam focuses on managing and maintaining Kubernetes clusters, while the Developer exam is focused on designing and deploying applications on Kubernetes. - How long is the Kubernetes Certified Administrator exam?
The exam is 3 hours long and consists of multiple practical scenarios. - Is Kubernetes suitable for enterprise environments?
Yes, Kubernetes is widely used in large-scale enterprise environments for its scalability and flexibility. - What tools should I use while preparing for the certification?
Use tools like kubectl, Minikube, Helm, and Kubernetes Dashboard. - How much experience do I need to take this exam?
Having at least 6 months to a year of practical experience with Kubernetes is recommended. - What is the cost of the certification?
The exam costs around $300. - Can I use online resources for practice exams?
Yes, there are several online platforms offering practice exams and tutorials. - What is the pass rate for this certification?
The pass rate is not officially disclosed, but preparation and hands-on practice are key.
List of Top Institutions Providing Kubernetes Training and Certifications
1. DevOpsSchool – A well‑known platform offering hands‑on Kubernetes training that prepares learners from basics to advanced Kubernetes operations. Their courses focus on real projects, live labs, and exam‑oriented curriculum for both CKA and developer paths.
2. Cotocus – A professional training and consulting organization that provides structured instruction on cloud native and DevOps technologies, including Kubernetes concepts, cluster management, and practical deployment strategies.
3. ScmGalaxy – A community‑driven institute offering in‑depth training on DevOps and related cloud‑native skills. Their programs help learners understand automation, containerization, and orchestration tools central to Kubernetes certification success.
4. BestDevOps – Focuses on delivering practical, fast‑track bootcamps and certification prep, integrating Kubernetes fundamentals with real‑world DevOps workflows to build job‑ready skills.
5. DevSecOpsSchool – Specializes in security‑integrated DevOps and complements Kubernetes training by teaching secure configuration, compliance testing, and secure automation approaches essential for production environments.
6. SRESchool – Offers Site Reliability Engineering training that aligns closely with Kubernetes operations and reliability best practices, helping learners manage highly available clusters effectively.
7. AiOpsSchool – Provides education on applying AI/ML techniques to IT operations, enhancing observability and automation skills which are valuable when working with Kubernetes in dynamic environments.
8. DataOpsSchool – Focuses on applying DevOps principles to data workflows. While not Kubernetes‑specific, its training helps professionals understand containerized data pipelines and infrastructure automation which boosts overall Kubernetes competence.
9. FinOpsSchool – Teaches cloud cost optimization and FinOps practices that are increasingly relevant when deploying and managing Kubernetes workloads in production, especially on public clouds.
Conclusion
The Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer certifications are invaluable for professionals looking to advance their careers in cloud-native technologies, DevOps, and software development. Whether you’re managing clusters, deploying applications, or ensuring system reliability, mastering Kubernetes equips you with the skills to tackle modern challenges in distributed systems.By earning these certifications, you’ll not only enhance your technical proficiency but also boost your career prospects in high-demand roles like DevOps Engineer, Cloud Engineer, and Kubernetes Specialist. With the right preparation, hands-on experience, and understanding of the exam objectives, you can confidently pursue these certifications and unlock new career opportunities.