
Welcome to the Dyspnea Information Hub of Best Cardiac Hospitals, your go-to resource for understanding the complexities of shortness of breath, medically termed dyspnea. This condition, which can manifest as an acute episode or a chronic issue, is often more than just discomfort—it’s a signal that something deeper may be affecting your respiratory or cardiovascular systems. Whether dyspnea arises during physical activity, rest, or sleep, it can interfere with daily life and may point to a wide range of underlying medical conditions that need attention.
Dyspnea, or shortness of breath, is a distressing sensation where breathing feels difficult or inadequate. It is often described as a feeling of not getting enough air, tightness or heaviness in the chest, or struggling to catch one’s breath. While occasional shortness of breath after intense physical activity is normal, experiencing dyspnea during mild exertion or even at rest can be a sign of an underlying health problem that requires attention.
Dyspnea is not a disease in itself but a symptom associated with various medical conditions. It can range from a temporary and mild inconvenience to a chronic or life-threatening issue. Causes may include respiratory problems like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or pneumonia, as well as cardiovascular conditions such as heart failure, arrhythmias, or pulmonary embolism. Other factors, such as anemia, obesity, or high levels of anxiety, can also trigger dyspnea. Recognizing the circumstances and severity of shortness of breath is crucial, as it helps in diagnosing and addressing the root cause effectively. Prompt evaluation and appropriate treatment can alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent serious complications.

Dyspnea, or shortness of breath, manifests in different forms depending on its onset, duration, and underlying causes. Identifying the type of dyspnea is critical for diagnosing and managing the root condition effectively. Below are the primary types of dyspnea:
Characteristics: Sudden and severe onset of breathlessness that can appear within minutes or hours.
Common Causes: Infections like pneumonia, asthma attacks, pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lung), heart attacks, or anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction).
Urgency: Acute dyspnea is often a medical emergency and requires immediate attention to prevent complications.

Characteristics: Persistent shortness of breath lasting for weeks, months, or even years. It can range from mild discomfort to severe difficulty breathing.
Common Causes: Chronic conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, heart failure, or obesity.
Impact: Chronic dyspnea significantly affects daily life, limiting physical activity and overall quality of life.
Characteristics: Shortness of breath triggered by physical activity, even mild exertion like walking or climbing stairs.
Common Causes: Often associated with conditions that reduce oxygen supply, such as anemia, cardiovascular diseases, or lung disorders.
Significance: May serve as an early warning sign of heart or lung conditions, prompting the need for further evaluation.

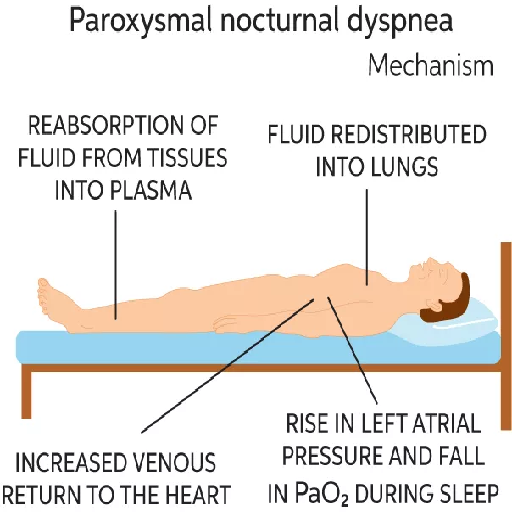
Characteristics: Sudden episodes of breathlessness that wake you from sleep, often accompanied by coughing or a feeling of suffocation.
Common Causes: Frequently linked to heart failure, particularly when fluid builds up in the lungs (pulmonary congestion) while lying flat.
Management: Patients may find relief by sitting upright or using extra pillows during sleep, but medical intervention is necessary for long-term management.
Dyspnea has a wide range of causes, which can be classified into heart-related, lung-related, and other medical or environmental factors.
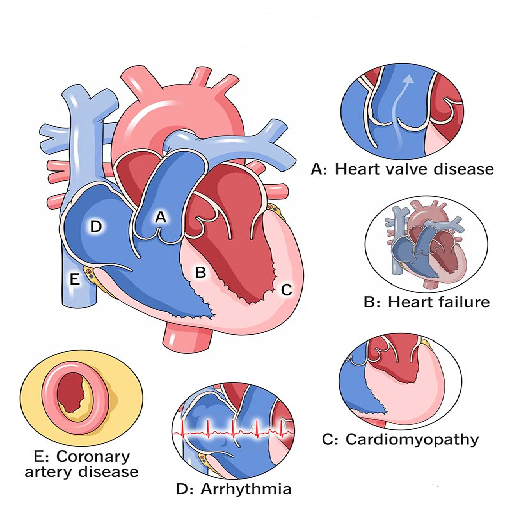
Heart Failure: The heart’s inability to pump blood effectively leads to fluid buildup in the lungs.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Reduced blood flow to the heart can trigger breathlessness, especially during exertion.
Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats can compromise blood oxygenation and cause shortness of breath.
Pericarditis: Inflammation of the heart’s lining can restrict its ability to function, causing dyspnea.
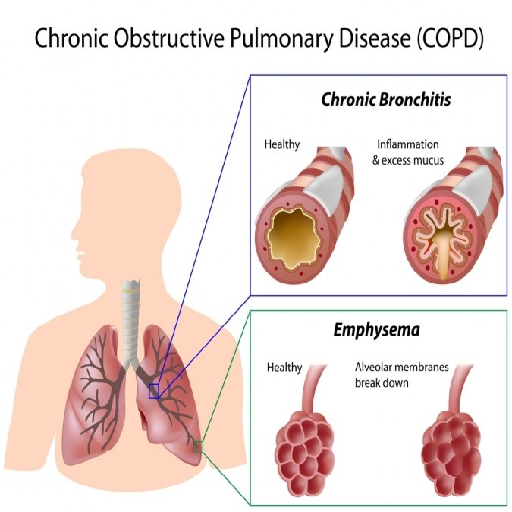
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A progressive lung disease that includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
Asthma: Narrowing of airways during an asthma attack can cause acute dyspnea.
Pulmonary Embolism: A blood clot in the lungs blocks blood flow and oxygen exchange.
Pneumonia: Infection in the lungs leads to inflammation and reduced lung function.
Interstitial Lung Disease: Scarring of lung tissue makes breathing difficult.
The primary symptom of dyspnea is difficulty breathing, but it can present in different ways:

An inability to take a deep breath or "catch your breath" comfortably or fully.

A sensation of pressure, tightness, or heaviness in the chest.

Breathing faster than usual during activity or at rest due to exertion.

A whistling sound during breathing or audible effort to inhale.
The treatment of dyspnea, or shortness of breath, is tailored to address the underlying cause. A correct diagnosis is crucial for effective management, as dyspnea can stem from heart-related issues, lung conditions, or other factors. Here’s a breakdown of the primary approaches:
When dyspnea is linked to cardiovascular conditions, treatments aim to improve heart function and reduce strain on the heart and lungs:
For dyspnea caused by respiratory conditions, treatments focus on opening airways, reducing inflammation, and improving lung function:
While not all cases are preventable, you can reduce your risk by addressing common triggers and maintaining good overall health:

Manage heart disease, asthma, or COPD with your doctor’s guidance.

Minimize exposure to smoke, dust, chemical fumes, and pollutants.

Reduce anxiety with relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.

Support cardiovascular and respiratory health with nutrient-rich foods.
At Best Cardiac Hospitals, our dedicated team of specialists is committed to providing compassionate care and advanced solutions. Whether you require immediate intervention for acute symptoms or a comprehensive plan for managing chronic conditions, we are here to support you every step of the way. From cutting-edge diagnostic tools to personalized treatment strategies, we aim to empower you with the resources and confidence to breathe easier and live healthier.